- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Industry News
- >
- High Voltage Diode Half- Wave Rectifier
High Voltage Diode Half- Wave Rectifier
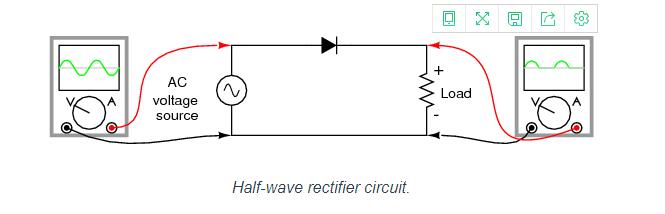
Half-Wave Rectifier
For most power applications, half-wave rectification is insufficient for the task. The harmonic content of the rectifier’s output waveform is very large and consequently difficult to filter. Furthermore, the AC power source only supplies power to the load one half every full cycle, meaning that half of its capacity is unused. Half-wave rectification is, however, a very simple way to reduce power to a resistive load. Some two-position lamp dimmer switches apply full AC power to the lamp filament for “full” brightness and then half-wave rectify it for a lesser light output. (Figure below)
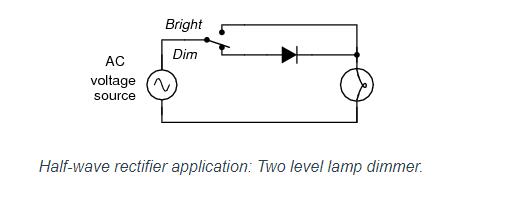
In the “Dim” switch position, the incandescent lamp receives approximately one-half the power it would normally receive operating on full-wave AC. Because the half-wave rectified power pulses far more rapidly than the filament has time to heat up and cool down, the lamp does not blink. Instead, its filament merely operates at a lesser temperature than normal, providing less light output. This principle of “pulsing” power rapidly to a slow-responding load device to control the electrical power sent to it is common in the world of industrial electronics. Since the controlling device (the diode, in this case) is either fully conducting or fully nonconducting at any given time, it dissipates little heat energy while controlling load power, making this method of power control very energy-efficient. This circuit is perhaps the crudest possible method of pulsing power to a load, but it suffices as a proof-of-concept application.